
The skyrocketing inflation and ongoing crisis in the forex market are putting serious pressure on the bank’s interest rate spread, which indicates shrinking profits. Spread is the difference between the interest that a bank charges a borrower and the interest a bank pays a depositor.
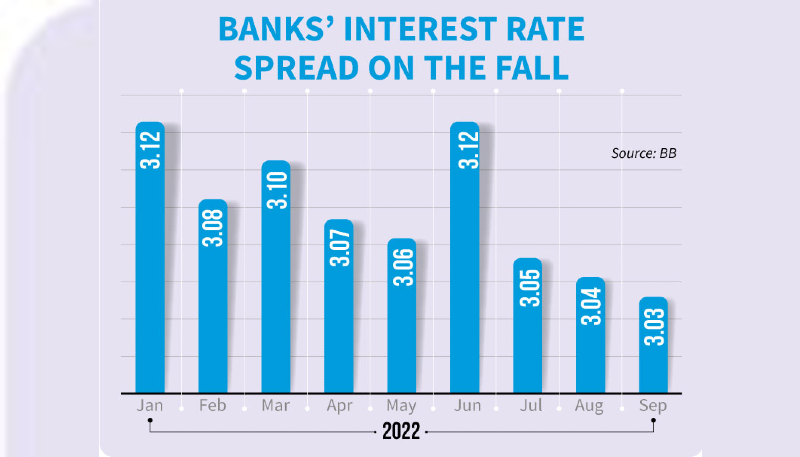
According to the latest data from the Bangladesh Bank, the overall interest rate spread of banks stood at 3.03 percentage points in September, down from 3.04 percentage points in the previous month.
The interest rate spread was 3.12 percentage points in January this year. This figure was at 3.16 percentage points in September of last year.
Industry insiders told The Business Post the interest rate spread continues to fall in recent times mainly due to the growing inflation and ongoing crisis in the foreign exchange market.
Most of the banks have raised their interest rate on deposits because of the high inflation, which had a negative impact on the interest rate spread, they added.
In September, the weighted average interest rate on deposit stood at 4.09 percentage points, up from 4.07 percentage points in August, as per the central bank data.
“We raised the interest rate on deposits to make adjustments with the inflation rate, which was the main reason for the downward trend of interest spread,” said Mohammad Ali, managing director and chief executive officer (current charge) of Pubali Bank.
The central bank in August last year had asked banks not to set interest rates on fixed-term deposits below the inflation rate.
Bangladesh’s overall inflation was 7.56 per cent in June, 7.48 per cent in July, 9.5 per cent in August and 9.1 per cent in September this year. The overall inflation rates recorded in August and September are both eleven-year-high figures.
Commenting further on the situation, Mohammad Ali said, “Profits from interest income continue to fall due to the high inflation rate. The interest rate of deposit has now risen to 7 per cent and it will grow further because of the central bank’s instructions in this regard.
“The ongoing crisis in the forex market is also another reason for the pressure. I am however optimistic that the crisis will end next year. In the current situation, the interest rate cap on loans needs to be withdrawn to tackle the downward trend of interest spread.”
Dhaka Bank’s Managing Director Emranul Huq said, “There is now a tight situation regarding funds in the banking sector, triggered by a forex crisis. The import financing and USD purchasing spree were the reasons behind the precarious situation.
“When funds become dearer in banks, they offer high-interest rates on deposit.”
The country’s banks purchased over $5 billion from the central bank by paying the equivalent amount of local currency Taka from July to November 5 to cover import payments.
The interest rate spread situation was different amid the pandemic period, which was reflected in a central bank financial stability report. According to the report, the overall interest rate spread stood at 3.20 per cent at the end of 2021, up from 3.10 per cent at the end of 2020.
Central bank officials said the deposit rate was very low amid the pandemic period and which was the reason for the improvement in spread. At the end of December last year, weighted average deposit rate registered at 3.99 per cent, down from 4.50 per cent posted a year ago.